How to operate a drone safely and effectively is crucial for both recreational and professional users. This guide provides a step-by-step approach, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced maneuvers and legal considerations. We’ll explore the intricacies of drone navigation, camera operation, and maintenance, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently take to the skies.
From understanding your drone’s controls and navigating different flight modes to mastering advanced techniques like waypoint navigation and obstacle avoidance, this comprehensive guide will empower you to capture stunning aerial footage and explore the exciting world of drone technology responsibly. We will also delve into the legal aspects of drone operation, ensuring you remain compliant with all relevant regulations.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for safe and responsible drone operation. It minimizes risks and ensures your flight is compliant with regulations. This involves a systematic inspection of your drone and its surroundings, followed by adherence to established safety protocols.
Pre-Flight Inspection Steps
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection should be performed before every flight. This process ensures all systems are functioning correctly and reduces the likelihood of malfunctions mid-flight.
- Visual Inspection: Carefully examine the drone’s body, propellers, and landing gear for any damage, loose parts, or debris.
- Battery Check: Verify battery levels are sufficient for the planned flight duration and that the battery is properly connected.
- Gimbal and Camera Check: Ensure the gimbal moves freely and the camera is securely mounted and functioning correctly. Check the camera settings (resolution, frame rate, etc.)
- GPS Signal Acquisition: Allow sufficient time for the drone to acquire a strong GPS signal before takeoff. This is especially important for features like Return-to-Home (RTH).
- Controller Check: Confirm the controller is fully charged and properly connected to the drone. Test the controls to ensure responsiveness.
- Software Updates: Check for any firmware updates for both the drone and controller. Updating ensures optimal performance and access to new features.
- Environmental Assessment: Evaluate weather conditions (wind speed, precipitation, visibility) and ensure they are suitable for safe flight.
Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Responsible drone operation requires adherence to local regulations and best practices. Familiarize yourself with these rules before each flight.
- Maintain visual line of sight with your drone at all times.
- Never fly near airports, heliports, or other restricted airspace.
- Respect people’s privacy and avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Fly only during daylight hours or in well-lit areas.
- Be aware of the surrounding environment and avoid obstacles.
- Never fly under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
- Register your drone with the appropriate authorities (if required in your region).
Pre-Flight Checklist Table
| Item | Check | Notes | Action Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drone Body | Inspect for damage | Repair or replace if necessary | |
| Propellers | Check for cracks or damage | Replace if damaged | |
| Battery Level | Ensure sufficient charge | Charge battery if needed | |
| GPS Signal | Confirm strong signal | Wait for signal acquisition | |
| Controller Connection | Verify connection | Reconnect if necessary | |
| Weather Conditions | Wind speed, visibility | Postpone flight if conditions are unsuitable |
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Mastering drone controls is essential for safe and efficient flight. Understanding the various controls, flight modes, and calibration processes will significantly improve your piloting skills.
Basic Drone Controls
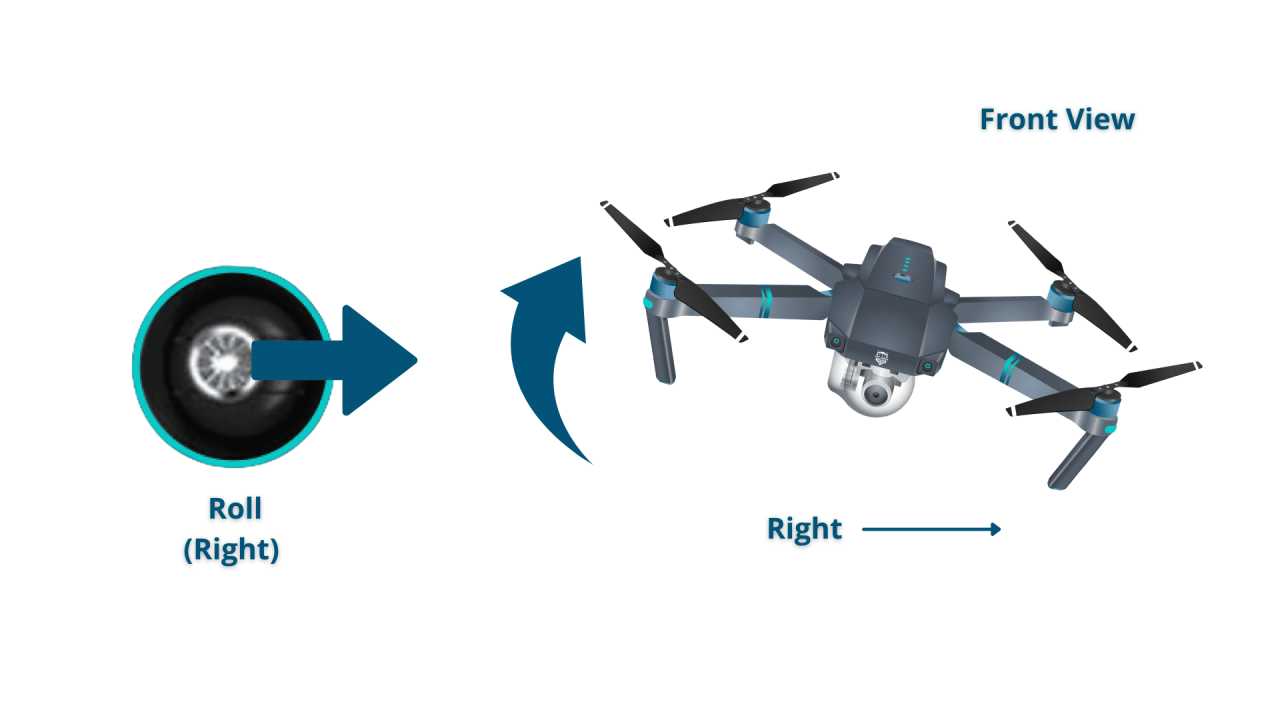
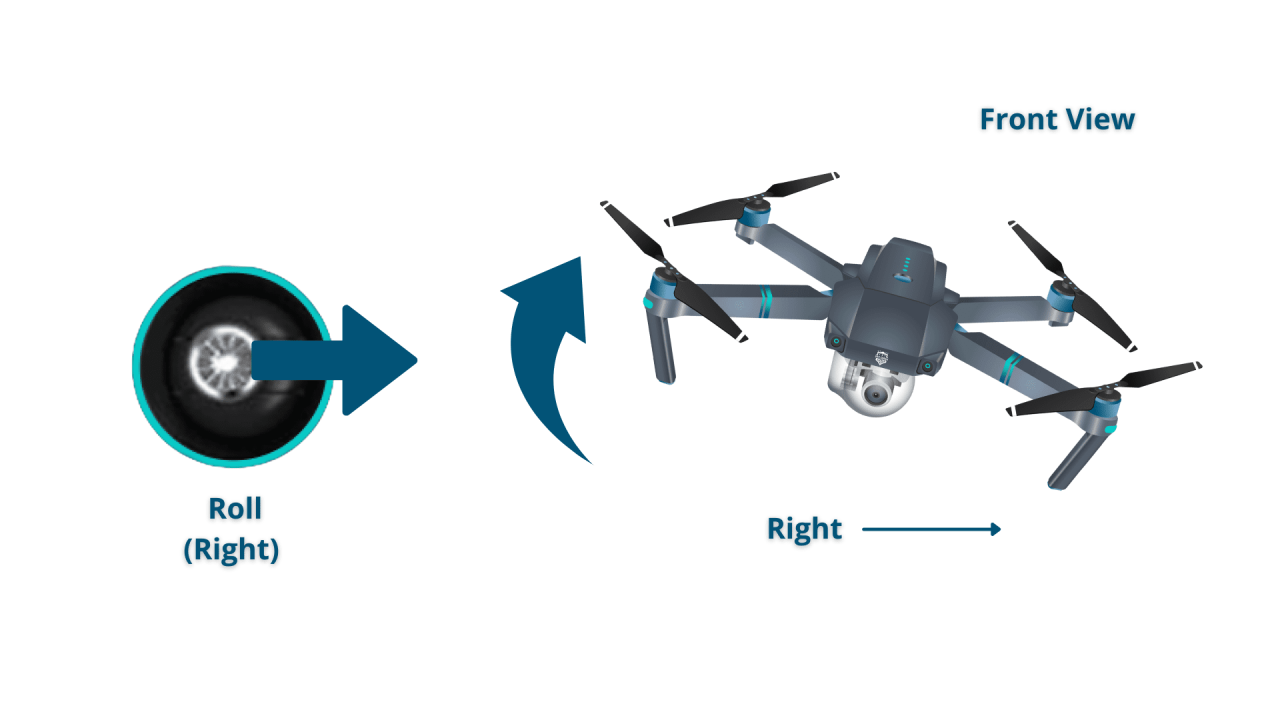
Most drones utilize two control sticks and various buttons. The left stick typically controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the right stick manages forward/backward and left/right movement.
- Left Stick: Vertical movement (up/down) and Yaw (rotation).
- Right Stick: Forward/backward and left/right movement.
- Buttons: These control various functions like taking photos/videos, switching flight modes, and activating Return-to-Home.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability. Understanding these modes is crucial for adapting to different situations.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains the drone’s orientation relative to the pilot. Ideal for beginners.
- GPS Mode: Uses GPS for positioning and stability. Allows for more precise control and features like RTH.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): Automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point. A crucial safety feature.
Drone Maneuvering Techniques
Smooth and controlled maneuvering requires practice and understanding of the drone’s response to control inputs. Start with slow, deliberate movements and gradually increase speed and complexity as you gain experience.
Drone Control Interface Comparison
Different drone manufacturers offer unique control interfaces. Some might prioritize simplicity, while others offer advanced features and customization options. Understanding the differences is important for selecting a drone that suits your skill level and needs.
Compass Calibration

Calibrating the drone’s compass ensures accurate positioning and navigation. This is a crucial step before every flight, especially in areas with magnetic interference.
- Power on the drone and place it on a level surface away from any metal objects or electronic devices.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to initiate the compass calibration process (usually involves rotating the drone 360 degrees).
- Monitor the on-screen indicators to ensure successful calibration.
- If the calibration fails, repeat the process or seek assistance from the manufacturer.
Taking Off, Landing, and Basic Flight Maneuvers: How To Operate A Drone
Proper takeoff and landing procedures, along with mastering basic maneuvers, are fundamental for safe and efficient drone operation. These procedures should be practiced in a safe, open area before attempting more complex flights.
Takeoff Procedure
A smooth and controlled takeoff minimizes the risk of accidents. Always ensure a clear and unobstructed takeoff area.
- Place the drone on a level, stable surface.
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Wait for GPS signal acquisition.
- Slowly and gently lift the drone using the left control stick.
- Maintain a stable hover before proceeding to other maneuvers.
Landing Techniques
Safe and efficient landing techniques are just as important as takeoff procedures. A controlled descent prevents damage to the drone and its surroundings.
- Begin the descent slowly and steadily using the left control stick.
- Maintain a slow and controlled descent to avoid a sudden impact.
- Gently lower the drone to the ground.
- Power off the drone and controller.
Basic Flight Maneuvers, How to operate a drone
Mastering basic maneuvers is crucial before attempting more advanced flight techniques. Practice each maneuver until you are comfortable and confident in your control.
- Hovering: Maintaining a steady position in the air. This is the foundation for all other maneuvers.
- Ascending: Moving the drone vertically upwards.
- Descending: Moving the drone vertically downwards.
- Turning: Rotating the drone around its vertical axis.
- Forward/Backward/Sideways Movement: Controlling the drone’s horizontal movement in all directions.
Takeoff and Landing Zone Diagram
The ideal takeoff and landing zone is a flat, open area free from obstacles and hazards. It should provide ample space for the drone to maneuver safely.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and practicing safe flight procedures. Learning the basics is crucial before taking to the skies, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures responsible and enjoyable drone operation.
+-----------------+
| |
| Landing |
| Zone | <-- Clear, flat area
| |
+-----------------+
^
|
| Takeoff Direction
|
v
+-----------------+
| |
| Takeoff |
| Zone | <-- Clear, flat area
| |
+-----------------+
Advanced Flight Techniques and Features
Once you've mastered the basics, exploring advanced flight techniques and features will unlock new creative possibilities.
These features enhance both the safety and capabilities of your drone.
Advanced Flight Features
Modern drones offer various advanced features that significantly improve flight capabilities and safety.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Learning how to control the drone itself is paramount, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone. This comprehensive guide will help you confidently and safely operate your drone, ensuring you're well-prepared for your next flight.
Proper operation is crucial for both safety and effective results.
- Waypoint Navigation: Pre-programming a flight path for autonomous flight.
- Obstacle Avoidance: Sensors that detect and avoid obstacles automatically.
- Follow Me Mode: The drone automatically follows a designated subject.
Camera Angles and Settings
Adjusting camera settings and angles is crucial for capturing high-quality aerial footage. Experiment with different settings to find what works best for your specific needs.
Complex Flight Path Planning
Planning a complex flight path involves careful consideration of factors like battery life, airspace restrictions, and potential obstacles. Utilize flight planning software or apps to assist in this process.
Comparison of Drone Models
Different drone models offer varying capabilities regarding advanced features. Consider your specific needs and budget when selecting a drone.
Autonomous Flight Modes: Benefits and Limitations
- Benefits: Increased efficiency, automated tasks, hands-free operation, improved safety in certain scenarios.
- Limitations: Dependence on GPS and sensors, potential for malfunctions, limited control, suitability for specific environments.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its continued safe operation. A proactive approach can prevent costly repairs and ensure your equipment remains in top condition.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
Understanding common malfunctions and their causes allows for quicker diagnosis and resolution of problems.
- Propeller damage: Impacts, collisions, or wear and tear.
- Battery issues: Low charge, damage, or improper storage.
- Gimbal malfunction: Mechanical failure, software glitches, or impacts.
- GPS signal loss: Interference, poor weather conditions, or faulty GPS module.
Cleaning and Maintenance
Regular cleaning and maintenance of drone components are essential for optimal performance and longevity. Use appropriate cleaning materials and follow the manufacturer's guidelines.
Safe Storage and Transportation
Proper storage and transportation prevent damage and ensure the drone's safety during transit. Use a protective case or bag to shield it from impacts and environmental factors.
Battery Care
Proper battery care is critical for maintaining performance and lifespan. Avoid extreme temperatures, overcharging, and deep discharges.
Troubleshooting Guide Table
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drone won't power on | Low battery, faulty battery, power switch issue | Charge battery, replace battery, check power switch | Regular battery checks, proper storage |
| GPS signal lost | Interference, poor weather | Move to a location with better GPS signal, wait for better weather | Fly in open areas with good GPS reception |
| Propeller malfunction | Damage, loose screws | Replace damaged propellers, tighten screws | Regular inspections |
| Gimbal issues | Calibration issues, physical damage | Recalibrate gimbal, repair or replace | Avoid impacts |
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Understanding and adhering to all relevant laws and regulations is paramount for responsible drone operation. Ignoring these regulations can lead to legal consequences and potentially endanger others.
Relevant Regulations and Laws
Drone regulations vary by location. Familiarize yourself with the specific rules and regulations in your area before flying.
Permits and Licenses

In some regions, obtaining permits or licenses is required for operating drones, especially for commercial purposes or in restricted airspace.
Airspace Restrictions and No-Fly Zones
Many areas have designated no-fly zones due to safety concerns or security restrictions. These zones must be strictly respected.
Legally Restricted Scenarios
Several scenarios can legally restrict drone operation, including flying near airports, sensitive infrastructure, or during emergencies.
Flying Near Populated Areas or Sensitive Locations
- Obtain necessary permissions.
- Maintain a safe distance from people and structures.
- Be mindful of privacy concerns.
- Adhere to all local regulations.
Drone Photography and Videography Basics
Capturing stunning aerial footage requires understanding basic photography and videography principles, along with utilizing your drone's capabilities effectively.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Adjusting camera settings based on lighting conditions is crucial for optimal image quality. Experiment with ISO, shutter speed, and aperture to achieve the desired exposure.
Composition Techniques
Effective composition techniques enhance the visual appeal of your aerial footage. Utilize the rule of thirds, leading lines, and other compositional guidelines.
Achieving Smooth and Stable Video
Smooth and stable video is essential for professional-looking footage. Utilize features like electronic image stabilization (EIS) and gimbal stabilization.
Planning Shots and Creating Visual Narratives
Plan your shots in advance to create a compelling visual narrative. Consider the overall story you want to tell and how your shots will contribute to it.
Effects of Camera Angles and Perspectives
Different camera angles and perspectives create unique visual effects. Experiment with various angles to achieve the desired look and feel for your footage.
Mastering drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. By following the pre-flight checklists, understanding the controls, and practicing safe flight maneuvers, you can confidently explore the limitless possibilities of aerial photography and videography. Remember to always prioritize safety and legal compliance to ensure responsible and enjoyable drone flights. The sky's the limit – but remember to check the regulations first!
Popular Questions
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are available for beginners. Look for models with GPS, automatic return-to-home features, and intuitive controls.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies depending on the model and usage. Expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes on a single charge.
What happens if I lose signal with my drone?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. If signal is lost, the drone will attempt to return to its takeoff point. However, always fly within visual line of sight.
How do I clean my drone?
Use a soft, dry cloth to gently wipe down the drone's body. Avoid using harsh chemicals or water.
Can I fly my drone anywhere?
No. Airspace restrictions and no-fly zones exist. Check local regulations and use apps like B4UFLY to confirm safe flight locations.